The Import data application makes it possible to import specific data (e.g. items, countries, texts) from another Comarch ERP Enterprise system with the use of the Business Integration Service (BIS).
The Import data application consists of an application header, allowing the user to enter an import filter in the Filter field, and a work pane that displays attributes available for import that belong to the filter.
Except for filters saved in the database, it is also possible to use newly created filters. In order to use a new filter, it does not need to be saved. However, such a filter can be saved to make it reusable.
Saved filters are available in both the Import data and Export data applications, so they can be used for both import and export. Note that the data model of some business entities is different for import and export. Therefore, it is recommended to use different filters for import and export.
The Import items article contains procedures for working with the Import data application with regard to items; for instance, the article discusses the sequence in which items should be imported. Moreover, the article describes potential requirements and results of import operations.
More information on the Import data application, including the description of its fields and buttons, may be found in the Import data article.
The data exchange between Comarch ERP systems is described in detail in the Import data and Export data articles. This article describes data import from previous systems with the use of the Import data application.
The following import formats are available:
- XML is a file format characterized by the extensible markup language; it makes it possible to save data in a text file. The description language enables the definition, transfer, checking, and interpretation of data between applications and allows structured data exchange. Content, structure, and information are separated for presentation in XML documents. XML is coordinated and defined as a standard by W3C.
- CSV is a file format which contains text with separators; individual values are separated with commas. It is a file type in which the values of individual columns are delimited by a separator, while rows are delimited by line breaks. The separator must be known in order to import a given file. Frequent separators are, for example, the comma and the semicolon. Data saved in this format can be used and processed in numerous application programs.
- XLS is a file format which contains text separated with tabs. This file type is similar to CSV, except that the separator is a tab and the character encoding used is Unicode. Files in this format can be used in Microsoft Excel, among other applications.
If import is carried out in XML format, it is possible to import all requested data as part of a single import operation.
If import is carried out in CSV format, a different procedure is necessary. A technical limitation exists in that parallel 1:n relationships between business objects cannot be represented in one import file. That means, for example, that it is not possible to import inventory management and sales data from one file.
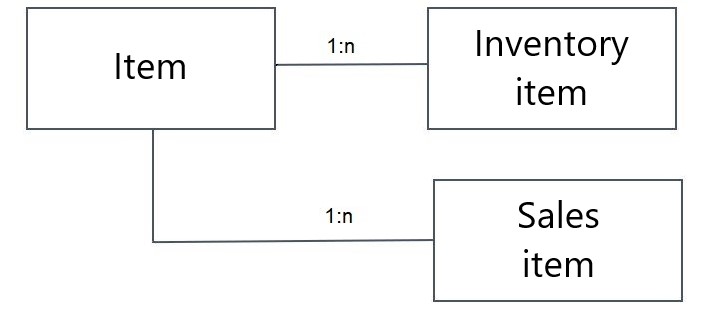
However, it is possible to import inventory management data and related warehouse data. There is a 1:n relationship between an item and its inventory management data as well as between the inventory management data and warehouse data. However, these are built one on top of the other and can therefore be imported from one file.

Procedures
The following chapter contains information about the requirements that must be met for importing item data and procedures for working with the Import data application:
- Importing data
- Necessary attributes for importing data from old systems
- Sequence
- Importing a new item
- Importing a new item view
- Importing an item view for a subordinate organization
- Importing an inherited structure
Importing data
In order to import item data:
- Open the Import data application
- Select the filter, or one of the filters, for the com.cisag.app.general.obj.Item business object. The filter and its attributes will be displayed in the work pane.
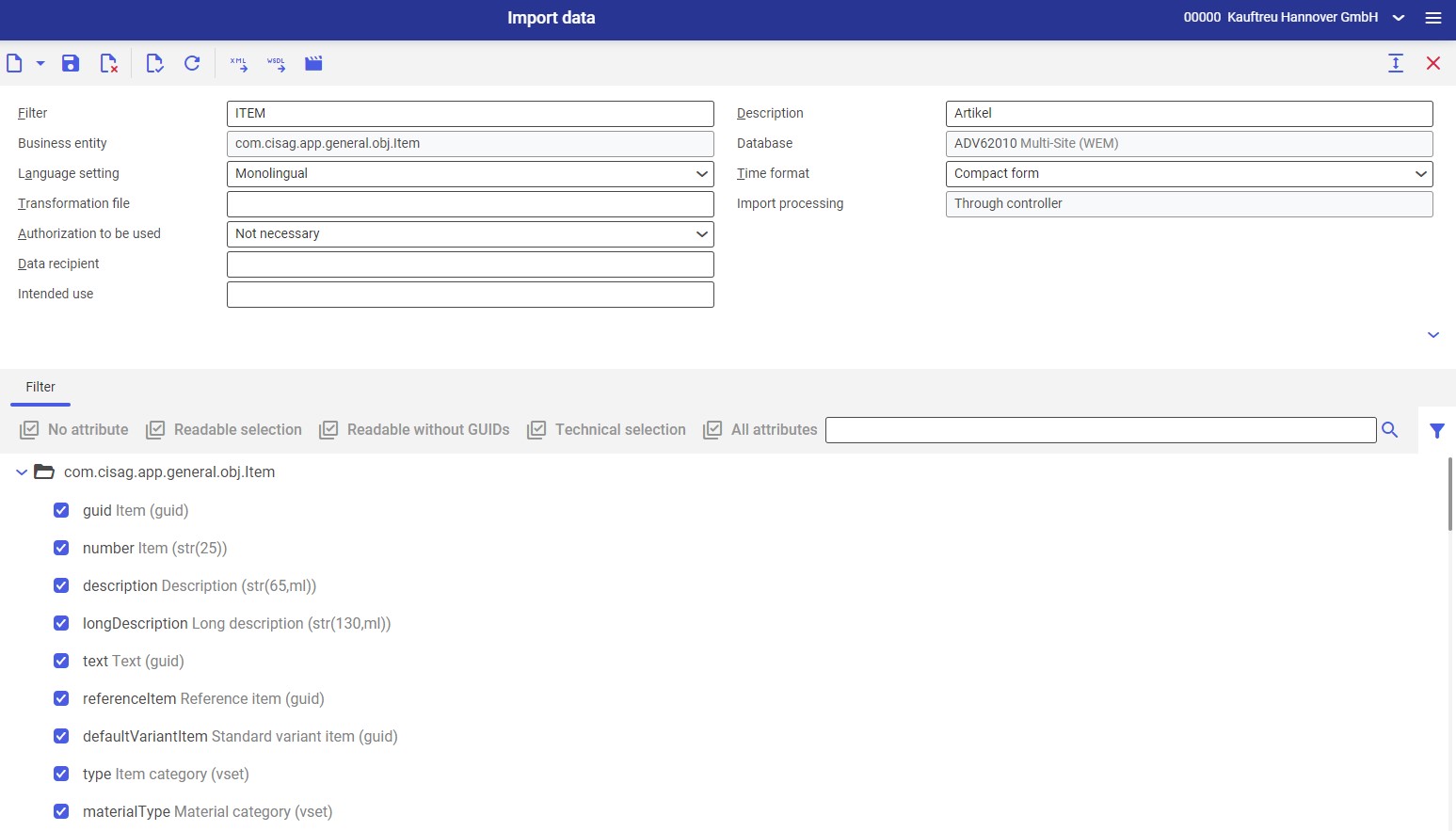
- Selected filter attributes will be displayed automatically. The user can additionally select those attributes that should be imported.
- Click the [Import data] button in the standard toolbar. The Import data dialog window will open.
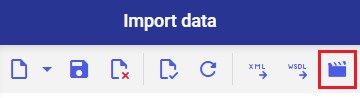
- The window makes it possible to configure import file settings. More information on the fields in the Import data dialog window may be found in the Import data article.
- Click the [In background] button to initiate import
Necessary attributes for importing data from old systems
When importing data from previous systems, it is necessary to specify the following attributes for each Item business object:
- Identification attributes (business key)
- Required fields
The Item business object cannot be assigned without identification attributes. The required fields and identification attributes of particular business objects are listed in the chapter Identification fields and required fields.
In addition, there are also relationships with other business objects that are not directly associated with the Item business object (relationships via external keys, which are labeled using italics in the filter). To resolve these relationships, the identification attributes of these business objects must be selected in the filter.
If the primary key of a business object consists solely or partly of external keys, the business object to which this external key refers must be resolved in the import file by means of its identification attributes.
Sequence
If the user wants to import data items that are dependent on one another, it is necessary to follow a defined sequence.
Standard sequence
- Base data
- Country data/Intrastat data (if this data is relevant based on the settings of the Customizing application)
- Financial data
- Purchasing and sales data
- Inventory management data
- Planning and production data
Item data for a supplier, customer, customer classification, and customer planning can be imported using separate import filters.
Sequence and additional conditions for a multi-site environment
In order to import a Purchasing, Sales, Inventory Management, Planning, or Production role, it is necessary to import the active OLTP client data before all other organizations.
The user must comply with the following sequence for each organization in the case of import operations: inventory management data must be imported before planning data and production data.
The data import can then be performed immediately or as a batch job. In the latter case, the system initiates processes. Also, the system determines the time at which these processes start. The user cannot influence the start time.
Importing a new item
Preconditions
- The destination system does not yet contain any items with a corresponding key
- A filter is available for the business entity com.cisag.app.general.obj.Item which contains attributes to be imported
Instructions
- Verify that the import file to be generated contains at least the item number (identification item)
- Ensure that all required fields (see the chapter Identification fields and required fields) of the base data are specified, to the extent possible
- Perform the steps as described in the chapter Importing data
Importing a new item view (at the active OLTP client level)
Preconditions
- The destination system already contains an item with the corresponding key. That is, the base data has already been imported.
- A filter is available for the business entity com.cisag.app.general.obj.Item which contains attributes to be imported
- An import file has been generated that contains the item number as an attribute
- The view data to be imported refers to the organization of the active OLTP client
Instructions
- Verify that the import file to be generated contains at least the item number (identification item) and the key of the view to be imported
- Ensure that all required fields (see the chapter Identification fields and required fields) of the view to be imported are specified, to the extent possible
- Perform the steps as described in the chapter Importing data
Importing an item view for a subordinate organization
Preconditions
- The system is a multi-site environment
- The destination system already contains an item with the corresponding key. That is, the base data has already been imported.
- Before the import is started, data for the relevant view at the active OLTP client level must already exist
- A filter is available for the business entity com.cisag.app.general.obj.Item which contains all readable attributes
Instructions
- Verify that the import file to be generated contains at least the item number (identification item) and the key of the view to be imported
- Ensure that all required fields (see the chapter Identification fields and required fields) of the view to be imported are specified, to the extent possible
- Ensure that the subordinate organization is authorized to maintain data for the view to be imported
- Perform the steps as described in the chapter Importing data
Importing an inherited structure
Preconditions
- The system is a multi-site environment or content-based authorizations are active. That is, there is more than one organization.
- The organization that is to inherit the data must be authorized for this view
- The organization must be a subordinate organization, that is, not the active OLTP client
- The destination system already contains an item with the corresponding key. That is, the base data has already been imported.
- At the level of the organization, data must already exist for the relevant view from which the destination organization is to inherit the data
- A filter is available for the business entity com.cisag.app.general.obj.Item which contains all readable attributes
Instructions
- Generate an import file that contains at least the item number (identification item) and the identification attributes of the imported object
- The inherited structure of the views is defined in the OrganizationalUnitItem business object. Each view having an inherited structure has a reference attribute in this business object:
| View | Reference attribute |
|---|---|
| Purchasing | MaintainingPurchasing |
| Inventory management | MaintainingInventory |
| Planning | MaintainingPlanning |
| Sales | MaintainingSales |
| Production | MaintainingProduction |
Enter the organization from which the destination organization is to inherit in the attribute for the relevant view.
- Make sure that the subordinate organization has the following authorizations:
- Authorization to maintain data for the view to be imported
- Authorization for the view to be imported (e.g. only a sales organization can inherit the Sales view)
- Perform the steps as described in the chapter Importing data
Special features for reference items
A reference item is used as a template for variants. A change in existing data or certain new data in the Items application causes a corresponding change in the associated variant items. The import of reference items is performed in the same way. More information on material types may be found in the Procedures: Items article.
Special features for variant items
A variant item always refers to a reference item. If the user wants to import a variant item, the related reference item must already exist in the database. In the case of variant items, it is only possible to import data that can be entered manually in the Items application. The user cannot create new views of variant items nor change or create an inherited structure. Also, it is not possible to change certain attributes via an import operation. Such data is controlled by the associated reference item. If the import file contains corresponding data, it is ignored during the import. However, the user can import a new variant item: more information may be found in the chapter Base data file for variant items.
Making changes via data import
The import functionality can also be used to make changes to existing item data. For instance, if the user wants to activate the availability check for all sales items, this can also be done via import.
Instructions
Generate a filter that contains the identification of a relevant item, the key attribute of a view, and the fields to be changed. Then, export the corresponding items, e.g. in CSV format. In the file created, change the corresponding field to the desired value. Then, import the file again with the generated filter. The following example illustrates the method for activating the availability check of a sales item:
| number | SalesItems.OrganizationalUnit | SalesItems.availabilityCheckActivated |
|---|---|---|
| 4711 | Active OLTP client | true |
| 4711 | Organization 1 | true |
| 4711 | Organization 2 | true |
| 4712 | Active OLTP client | true |
| 4712 | Organization 1 | true |
Deleting items or views
The import process can also be used to mark existing items or views for deletion. Likewise, a deletion marker can be deleted in this way. The import process then has the same effect as pressing the [Mark for deletion] or [Unmark for deletion] buttons in the Items application.
To set a deletion marker, the corresponding business object needs to be imported in the Delete mode. To remove a deletion marker, the corresponding business object also needs to be imported in the Delete mode. This mode can only be activated in XML format.
| XML | Effect |
|---|---|
| <Item xmlns=”com.cisag.app.general.obj.Item” mode=”delete”> <number>4711</number> </Item> | If item 4711 still has no deletion marker, it will now be marked in its entirety for deletion. That is, a deletion marker is also applied to all views in all organizations. If item 4711 already has a deletion marker, it will be removed again for the base data. The deletion marker for views is not removed. See also: Procedures: Items. |
| <Item xmlns=”com.cisag.app.general.obj.Item”> <number>4712</number> <PurchaseItems mode=”delete”> <OrganizationalUnit> Active OLTP client </OrganizationalUnit> </PurchaseItems> </Item> | If the Purchasing view of item 4712 still has no deletion marker at the organization level of the active OLTP client, the Purchasing view will now be marked in its entirety for deletion. The specification of data for the organization of the active OLTP client is sufficient. Any purchasing items created at the level of other organizations are also marked for deletion. If the Purchasing view of item 4712 already has a deletion marker at the level of the active OLTP client, this will be removed if possible. The deletion markers for purchasing data of other organization are not removed. See also: Procedures: Items, Purchasing view. |
| <Item xmlns=”com.cisag.app.general.obj.Item”> <number>4713 <PurchaseItems mode=”delete”> <OrganizationalUnit> 90000 </OrganizationalUnit> </PurchaseItems> </Item> | If the Purchasing view of item 4713 still has no deletion marker at the level of organization 90000, the Purchasing view at this organization level will be marked for deletion. If the Purchasing view of item 4713 already has a deletion marker at the level of organization 90000, this will be removed if possible. Any purchasing data entered at the level of other organizations is not affected in either of these cases. See also: Procedures: Items, Purchasing view. |
| <Item xmlns=”com.cisag.app.general.obj.Item”> <number>4714 <ItemAccountingData mode=”delete”> <OrganizationalUnit> 92000 </OrganizationalUnit> </ ItemAccountingData> </Item> | If the Financials view of item 4714 still has no deletion marker at the level of organization 92000, the Financials view at this organization level will be marked for deletion. If the Financials view of item 4714 already has a deletion marker at the level of organization 92000, this will be removed if possible. For financial data, every firm must enter its own data (that is, no inheritance is possible). Therefore, only the specified organization is ever affected in the case of financial data. See also: Procedures: Items, Planning view. |
Import with CSV files
For reasons of system performance, it is recommended to import as much information as possible in the first import operation, e.g. multiple item views and organizations. Individual files should have the following structure:
- The main file: it should contain all information on the required base data. This file specifies which item will be imported.
- Country data
- Financial data
- Sales data
In this file, it is important that the first line in which the item number changes always contain data for the active OLTP client organization. Data for subordinate organizations can then follow.
- Similarly as in the case of sales data, it is possible to create files containing other inheritable views. It is important here that the sequence of items in the individual files correspond to the sequence of items in the main file. Individual item numbers can be omitted in the additional files, e.g. if a given item is not to have a view.
References of files
Preconditions
- A filter is available for the business object cisag.app.general.obj.Item which contains attributes to be imported
- A main file containing the base data is available
- One or more additional files with additional data are available
- Each value of the referencing Item attribute must also be contained in the main file
Instructions for importing data with references of files
- Open the Import data application
- Select the filter, or one of the filters, for the com.cisag.app.general.obj.Item business object. The filter for the import of item data will be displayed.
- Selected filter attributes will be displayed automatically. If required, it is possible to select additional attributes for import.
- Click the [Import data] button in the standard toolbar. The Import data dialog window will open.
- The window makes it possible to configure import file settings. More information on the fields in the Import data dialog window may be found in the Import data article.
- Select the [Create links] button. Another dialog window will open.
- The user may create a new reference by specifying the object path, an additional file as the source file, the error file, and the referencing attribute (Attribute number for item import).
The object path describes the name of the relationship to the business object to be imported. One of the additional files is selected as the source file. Make sure that the connection to the additional file matches the object path information. If, for example, SalesItems is selected as the object path, the specified additional file should also contain the data for sales items. - Repeat steps 7 to 8 until all additional files are referenced
- Click the [Accept] button
- Click the [In background] button to initiate import
Examples
The structure of the base data file and the additional files is described below. To learn which attributes are required fields and must therefore be specified to the extent possible, see the chapter Identification fields and required fields.
Base data file
| number | description | ... |
|---|---|---|
| 4711 | Full description for 4711 | ... |
| 4712 | Full description for 4712 | ... |
| 4713 | Full description for 4713 | ... |
Base data file for variant items
The import of variant items is only possible if the associated reference item already exists. To import a new variant item, the following file is sufficient.
| number | description | type | materialType | ReferenceItem |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| v | Full description | MATERIAL | VARIANT_ITEM | REF1 |
This example will create a new variant item with the REF1VAR1 item number, which is based on the REF1 reference item. In a multi-site environment, the total organizational structure of the reference item will also be transferred to the variant item.
Country data file
| number | ItemCountry Data.Country | ItemCountry Data.mandatory | ItemCountryData.intrastat.IndexOfGoodsNumber | … |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4711 | true | 12101000 | ||
| 4711 | DE | true | 12102010 | … |
| 4711 | CH | false | … | |
| 4712 | false | … | ||
| 4713 | true | 10011000 | … | |
| 4713 | AT | false | … |
Item 4711 receives the standard record and, additionally, country data for Germany and Switzerland. Item 4712 receives only the standard record. Item 4713 receives the standard record and, additionally, country data for Austria.
Financial data file
| number | ItemAccountingData | ... |
|---|---|---|
| 4711 | Firm 1 | ... |
| 4711 | Firm 2 | ... |
| 4712 | Firm 3 | ... |
In this example, item 4711 receives financial data for Firm 1 and Firm 2 finance organizations. Item 4712 receives financial data for Firm 2 organization.
File for inheritable views
This example will specify the inheritable Sales view. The procedure is the same for the Purchasing, Inventory management, Planning, and Production views.
| number | SalesItems.OrganizationalUnit | ... |
|---|---|---|
| 4711 | Active OLTP client | ... |
| 4711 | Organization 1 | ... |
| 4711 | Organization 2 | ... |
| 4712 | Active OLTP client | ... |
| 4712 | Organization 1 | ... |
| 4713 | Active OLTP client | ... |
In this example, item 4711 receives sales data for Organization 1 and Organization 2 organizations. Item 4712 receives separate sales data for the active OLTP client and Organization 1. Item 4713 receives sales data only at the level of the active OLTP client.
Identification fields and required fields
The required fields and key attributes (K) of the individual business objects are listed below. The identification fields and required fields are subject to changes and can also be expanded by adaptations.
The following information is also available after opening the Items application, switching to the relevant view, and validating it with the [Validate] button. All fields exhibiting a red corner are required.
Base data
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| number (K) | Item |
| uoms[0] | Base unit |
| description | Full description |
| MaintainingOrganization (only necessary if the system is a multi-site environment or if content-based authorizations are active) | Organization responsible |
| ReferenceItem (only required for variant items) | Reference item |
If the item category (type attribute) and material category (materialType attribute) are not specified, a standard inventory item is assumed.
Country data
The specification of country data is only possible if the Intrastat parameter has been selected in Customizing → Country-specifics.
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| number (K) | Item |
| ItemCountryData.Country (K) | Country (or empty value or Zeroguid for defaults) |
| ItemCountryData.intrastat.mandatory | false = following attributes are optional true = following attributes are required |
| ItemCountryData.intrastat.CountryOfOrigin | Country of origin |
| ItemCountryData.intrastat.IndexOfGoodsNumber | Item number |
Financial data
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| number (K) | Item |
| ItemAccountingData.OrganizationalUnit(K) (Only necessary if the system is a multi-site environment) | Organization |
The specification of the organization is only required in a multi-site environment. If the organization is not specified in a single-site environment, the organization is set to that of the active OLTP client.
The following attributes of financial data are not required fields. However, their specification is recommended because they co-determine the lock status for the Purchasing, Inventory management, and Sales applications.
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| ItemAccountingData.inputTaxClassification | Input tax classification (for purchasing) |
| ItemAccountingData.outputTaxClassification | Value added tax classification (for sales) |
| ItemAccountingData.expenseClassification | Expense account classification (for purchasing) |
| ItemAccountingData.revenueClassification | Revenue account classification (for sales) |
| ItemAccountingData.cogClassification | Inventory account classification (for inventory management) |
Purchasing item data
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| number (K) | Item |
| PurchaseItems.OrganizationalUnit(K) | Organization |
| PurchaseItems.classification1 | Classification 1 |
The specification of the organization is only required in a multi-site environment. If the organization is not specified in a single-site environment, the organization is set to that of the active OLTP client.
If the uom[0] and pricingUom attributes are not specified, they are preassigned with the base unit of the item.
Inventory item data
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| number (K) | Item number |
| InventoryItems.OrganizationalUnit(K) | Organization |
| InventoryItems.classification1 | Classification 1 |
The specification of the organization is only required in a multi-site environment. If the organization is not specified in a single-site environment, the organization is set to that of the active OLTP client.
If the ABC classification is not specified, the value is set to A.
Planning data
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| number (K) | Item |
| ItemPlanningData.OrganizationalUnit(K) | Organization |
| ItemPlanningData.makeOrBuy | Demand coverage Available values include: - BUY (external purchasing) - BUY_INTERNAL (internal purchasing) - MAKE (production) |
The specification of the organization is only required in a multi-site environment. If the organization is not specified in a single-site environment, the organization is set to that of the active OLTP client.
Depending on the setting of the makeOrBuy attribute, one of the following tables is applied. The import of files must then also contain these attributes.
Non-specified attributes are assigned relevant default values. If the input file is not to contain any production data, the value for the useProductionData field must be set to false. The field is preassigned the value true.
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| ItemPlanningData.usePurchaseData | External purchasing (the value must be set as true) |
| ItemPlanningData.PurchasingOrganisation | Purchasing organization |
| ItemPlanningData.PurchasingScheduler | Purchasing scheduler |
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| ItemPlanningData.useInternalPurchaseData | Internal purchasing (the value must be set as true) |
| ItemPlanningData.InternalPurchasingOrganisation | Purchasing organization |
| ItemPlanningData.InternalDeliveryPartner | Source site (must be a logistics organization that is also a supplier to the specified purchasing organization) |
| ItemPlanningData.InternalPurchasingScheduler | Purchasing scheduler |
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| ItemPlanningData.useProductionData | Apply production data (the value must be set as true) |
| ItemPlanningData.Planner | Planner |
| ItemPlanningData.PurchasingScheduler | Production scheduler |
Sales item data
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| number (K) | Item number |
| SalesItems.OrganizationalUnit(K) | Organization |
| Sales.classification | Classification 1 |
The specification of the organization is only required in a multi-site environment. If the organization is not specified in a single-site environment, the organization is set to that of the active OLTP client.
If the uoms[0] and pricingUom attributes are not specified, they are preassigned with the base unit of the item.
Production item data
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| number (K) | Item number |
| ProductionItems.OrganizationalUnit(K) | Organization |
| ProductionItems.classification1 | Classification 1 |
The specification of the organization is only required in a multi-site environment. If the organization is not specified in a single-site environment, the organization is set to that of the active OLTP client.
If alternative production methods are permissible according to settings defined in the Customizing application:
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| ProductionItems.defaultProductionPlan.type | Category Values from the value set ProductionPlanKeyType (permitted values): - BOM = Bill of material - ROUTING = Bill of material and Routing - PROCESS = Bill of resources (BOR) |
| ProductionItems.defaultProductionPlan.BillOfMaterial.code | Bill of material Required field if category = Bill of material or Bill of material and Routing |
| ProductionItems.defaultProductionPlan.BillOfMaterial.type | Bill of material Required field if category = Bill of material or Bill of material and Routing Value = BILL_OF_MATERIAL |
| ProductionItems.defaultProductionPlan.Routing.code | Routing Required field if category = Bill of material and Routing |
| ProductionItems.defaultProductionPlan.Routing.type | Routing Required field if category = Bill of material and Routing Value = ROUTING |
| ProductionItems.defaultProductionPlan.Process.code | Bill of resources (BOR) Required field if category = Bill of resources (BOR) |
| ProductionItems.defaultProductionPlan.Process.type | Bill of resources (BOR) Required field if category = Bill of resources (BOR) Value = PROCESS |
If alternative production methods are not permissible according to settings defined in the Customizing application:
| Required field/Key attribute (K) | Field |
|---|---|
| ProductionItems.defaultProductionPlan.BillOfMaterial.type | Value = BILL_OF_MATERIAL |
