Topic overview
Item characteristics are used to describe the unique properties of items. The Item characteristics application can be used to assign fixed properties to existing items in the form of characteristic values. It is also possible to assign variable configuration characteristics to items, either in addition to the item characteristics or exclusively.
Below you will find information on the possible use of item characteristics and references to the applications in which relevant data must be entered for their use.
Definitions of terms
Item characteristics
Item characteristics are used to describe specific features of items. Item characteristics are assigned to item characteristic classifications. Any classification systems can be built up with the aid of definable item characteristic classifications. Item characteristics are adopted within a classification.
Item characteristic classification
Specially marked classification that is used to build up the logical structure of item characteristics. Any number of characteristics can be assigned to each classification node. The sum of the characteristics that can be used results from the characteristics of the node itself and all the characteristics of parent nodes on the path to the root of the classification.
Classifications
A classification represents the superordinate and subordinate relationship between objects. It determines the ranking order in the system. A classification can consist of several levels. Classifications consist of inter−dependent nodes. The higher, parent node in each case is called Folder. The node underneath the last folder is called Leaf.
Configuration characteristics
Configuration characteristics are variable properties of production items that have not yet been clearly specified. These properties are specified while creating a sales quotation, sales order or in the production order. The configuration characteristics can be used in the production structure for analysis of substitute functions, conditions and formulas, for example for dispatching production orders or calculation, and in planning.
Maximum routing
Maximum routing indicates all operations which are possible to be executed during the process of item production. Through conditions specified in the routing, only those operations which are necessary to produce a specific item, are selected.
Maximum bill of material
In maximum bill of material, all materials from which it is possible to produce an item, are nominated. With the help of conditions contained in the bill of material, only those materials which are necessary to produce a specific item, are selected.
Characteristic values
Characteristic values are the specific values that a characteristic can assume. Characteristics values can consist both of a selection of attributes, e.g., steel, carbon, or aluminum, and of any discrete values within a value range, e.g., 10.01, 12.19, or 28.00.
Areas of application
A typical task for the use of item characteristics is the entry of a sales order in which the customer does not specify the item number when ordering, but the characteristics of the product. A production order can be generated directly from this, in which the item characteristics are used as a condition. If items are assigned to a classification and item or configuration characteristics are defined, two main application possibilities can be derived from this:
- Configuration characteristics can be used, for example, to configure a production item that is available in different variants or properties (e.g. color, power, capacity). These can then be defined on an order-specific basis when entering a sales quotation, sales order, or in the production order. The configuration characteristics are used in the production structure for analysis of substitute functions, conditions, and formulas, e.g. when dispatching production orders or calculation, and in Planning.
- Item characteristics can also be used in the production structure. However, their primary use is for a convenient search. For example, you can use item characteristics to search for a sales item according to specific properties.
Item characteristics and configuration characteristics require a classification of the items. Item characteristics or configuration characteristics and the item characteristic classification belong together. Any number of classification systems can be set up using a freely definable item characteristic classification.
The item characteristic classification can be used to create any self-defined or standardized classifications (eCl@ss), as well as the classes made popular by DIN for standard parts (DIN 4000).
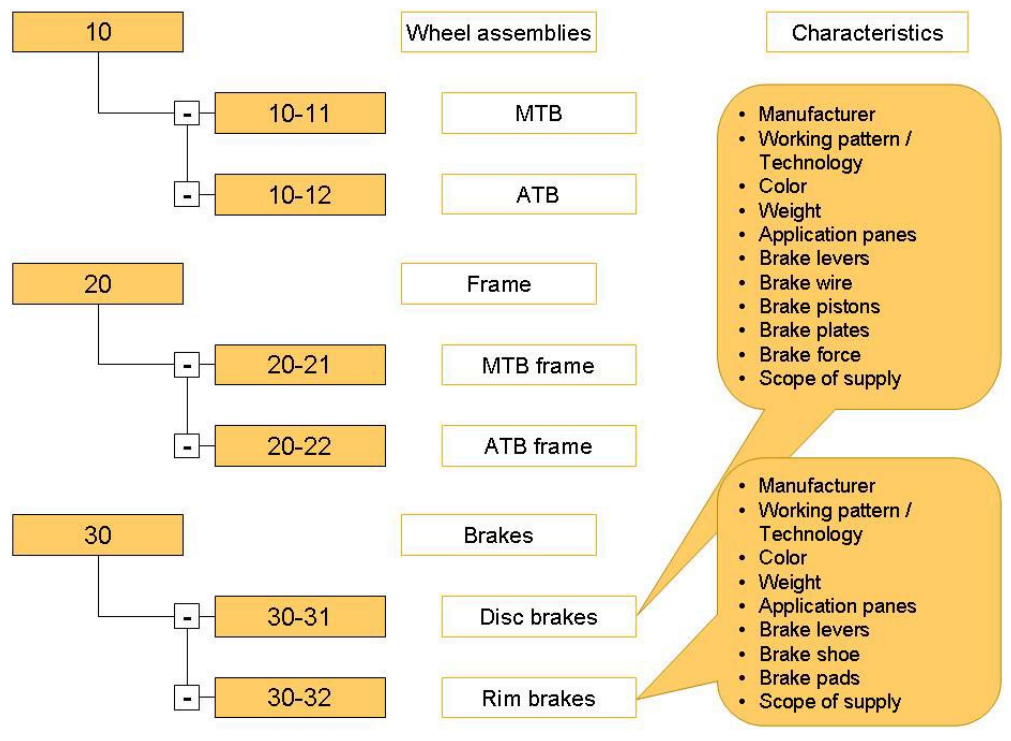
The Item characteristic classifications application is used to create a structure with assigned characteristics. The layout of the structure and the use of the item characteristics depend on the situation. Further information on the application can be found in the Item characteristic classifications article.
To create a structure, e.g. an item characteristics list, item characteristics are entered using the user-defined fields. These item characteristics are assigned to the nodes of the item characteristic classification. Items are assigned to the leaves of this structure. One item is linked to exactly one leaf.
Item characteristics are inherited within the structure. This means that an item inherits the item characteristics of all parent nodes.
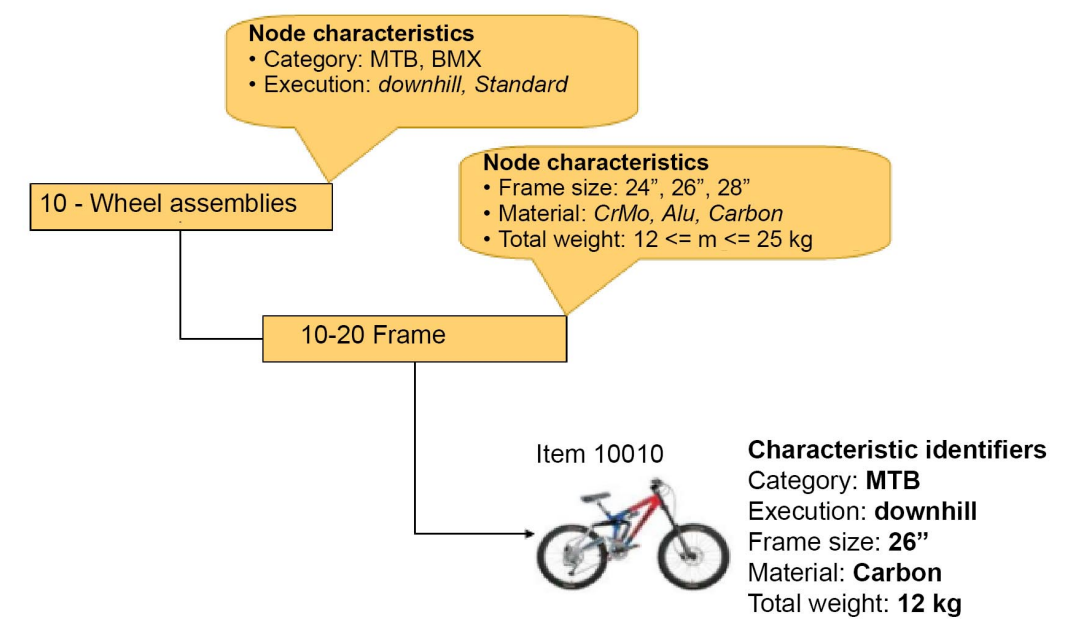
The actual values of the item characteristics (characteristic values) for the individual items are recorded in the Item characteristics application and saved separately from the item master data.
You can find instructions for handling item characteristics, configuration characteristics and classifications, e.g. how to enter an item characteristic classification with characteristics and characteristic values, in the article Procedures: Item characteristics.
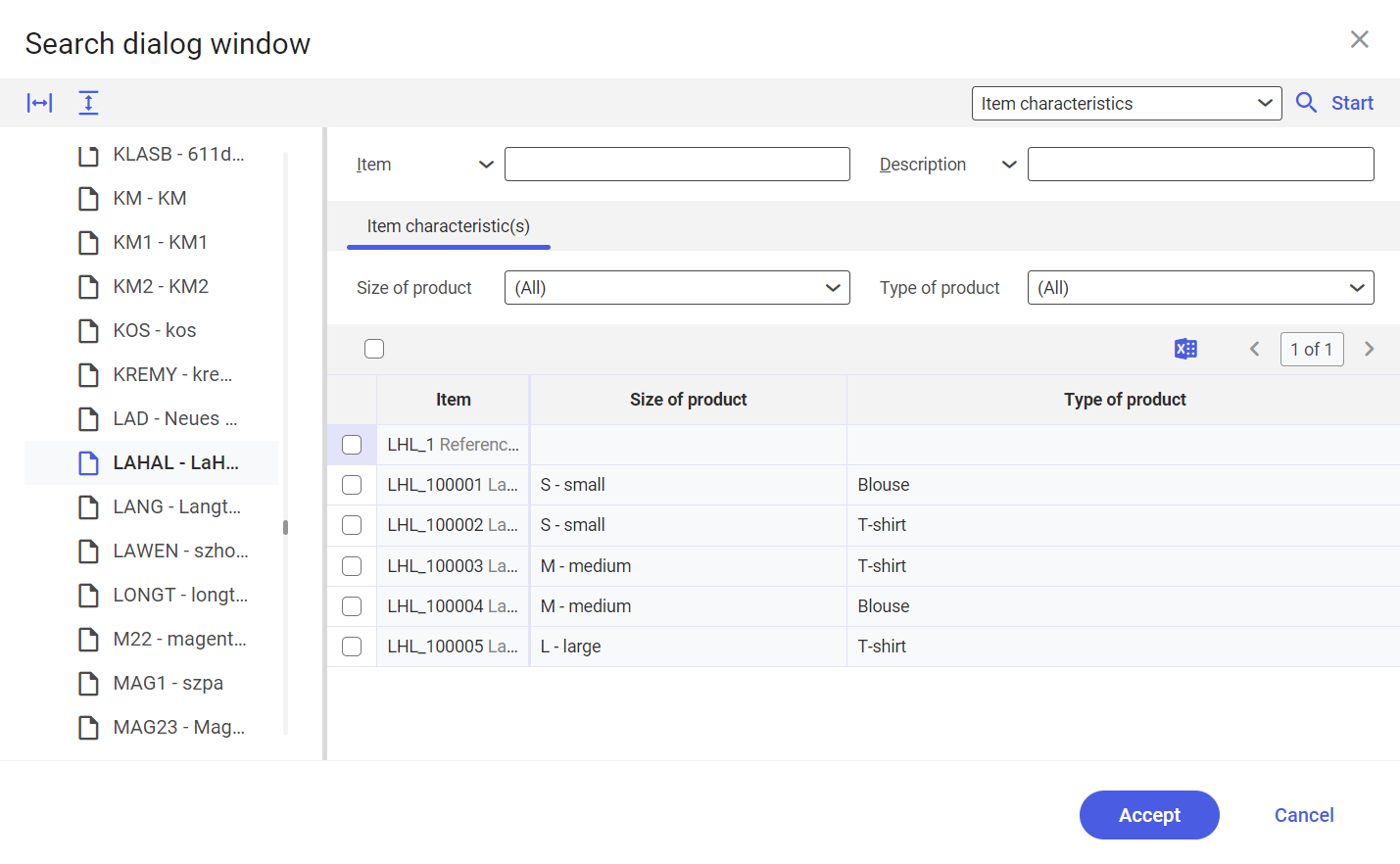
Item search according to item characteristics
In some applications, you are also offered the option of searching according to item characteristics in an item search. To do this, you can select the search according to item characteristics in the item search dialog window via a selection field in the toolbar of the window. After selecting the Item characteristics option, the structure of the dialog window changes: the item characteristic classifications entered are displayed in the left-hand area of the dialog window and the possible item characteristics of the selected item characteristic classification and a results list are displayed in the right-hand area.
If the available item characteristics are displayed in the right-hand area, you can enter the specific characteristics as search characteristics and start the search accordingly. The results list displays the items that match the search criteria you entered.
Examples of utilization of item and configuration characteristics
The following chapter describes examples of the utilization of item characteristics and configuration characteristics.
Item characteristic search when creating a sales order
Effective search for the correct item is supported by its properties (characteristics) while creating a sales order with items that are used in various models, such as a pump with different outputs, connecting dimensions, usages, pumping media etc. A practical use is creating multi-variant business items or production items with variant parts lists or routings.
This search based on characteristics is possible in all applications in which items can be searched through the value assistant. The sales order example acts as a representative description of necessary preconditions and procedures for other applications as well.
The following applications are affected:
- Item characteristic classifications
- Item characteristics
- Field types
- Sales orders
Item characteristic classifications application
In the Item characteristic classifications application, freely definable classification structures are created for which item characteristics can be entered at any node and leaf. Node characteristics are inherited at the level below it. In the line item editor, under the Item characteristics tab, you can assign existing characteristics to a node or leaf or enter new characteristics using the corresponding action.
A characteristic is created using a user-defined field. User-defined fields can be of different types. For example, it can be entered as a selection field that offers various values for selection. Further information on the application and procedures can be found in the articles Item characteristic classifications and Field types.
In order to be able to use item characteristics with their possible values to describe items, an item characteristic classification must exist.
Item characteristics application
In the Item characteristics application, the previously defined item characteristics are assigned to an item. The item characteristics are offered with their possible values. You can select the values depending on the characteristic type and use them to describe the specified item. Further information on the application can be found in the Item characteristics documentation.
In order for items to be searchable using item characteristics, it is required that item characteristics have been assigned to the items and a characteristic value has been defined.
Item search in the sales order
If you click the value assistant icon for the Item field in the line item editor of the Sales orders application, a dialog window for searching for items opens. In the toolbar of the window, you will find a selection field for the search options that are offered to you.
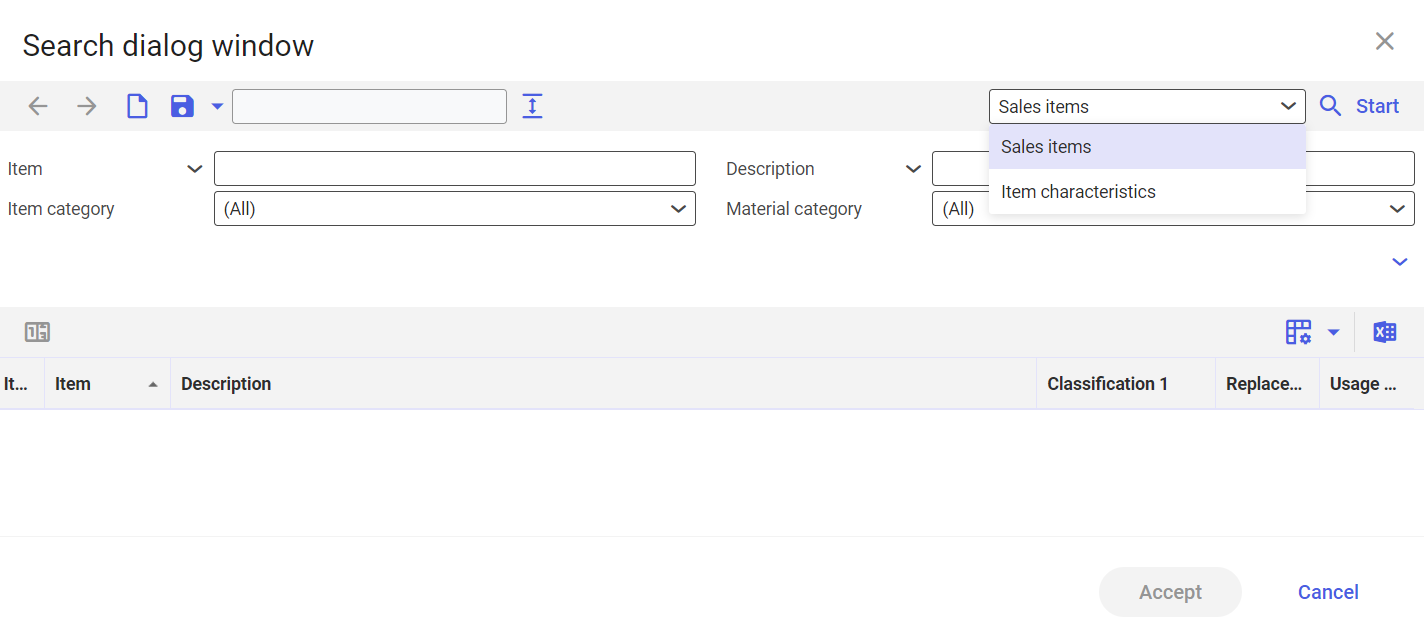
When you select the Item characteristics search, the structure of the dialog window changes:
In the left-hand area, you can select the classification. You can select both the characteristics of a node and those of a leaf.
In the right-hand area, you will find the query fields for the node or leaf of the selected classification and a results list below.
You can search for item identifications or use the item characteristics to search for items. Below the query fields, you will find the items that correspond to the values in the query fields after you have started the search.

Item configuration using configuration characteristics
When entering a configurable item in a production order, you can create order-specific product structures (bill of material, routing, use of resources) using configuration characteristics. In this way, structures are generated during the dispatching process. These structures only apply to this order. In this way, you can use a “minimum bill of material” to produce different items that are used in different models, e.g. a pump with different outputs, connecting dimensions, usages, pumping media, etc.
This option is also available when entering a sales order if you want to create order-specific production item structures in order to produce a sales item on the basis of the order.
The preconditions and procedures required for this are described below using the example of the production order.
The following applications are affected:
- Item characteristic classifications
- Item characteristics
- Field types
- Production orders
- Bills of material
- Operations
Item characteristic classifications application
In the Item characteristic classifications application, freely definable classification structures are recorded, as already described in the Item characteristic classification application chapter for searching with item characteristics. Unlike for item characteristics, however, configuration characteristics can only be entered for leaves.
In the line item editor under the Configuration characteristics tab, you can assign existing or new features to a leaf using the corresponding action.
A characteristic is created using a user-defined field. User-defined fields can be of different types. For example, it can be entered as a selection field that offers various values for selection. Further information on the application and procedures can be found in the articles Item characteristic classifications and Field types.
In order to be able to use item characteristics with their possible values to configure items, an item characteristic classification must exist.
Item characteristics application
In the Item characteristics application, an item is assigned the previously recorded configuration characteristics with which it could be configured. Unlike item characteristics, no values are offered for selection for configuration characteristics, as these are only selected when the item and its configuration are used. Further information on the application can be found in the Item characteristics documentation.
Utilization in the sales order
If you use the line item editor to enter a line item for which configuration characteristics must be selected, a dialog window opens before the line item is transferred to the line item table in order to define the configuration characteristics. This requires the following:
- At least one configuration characteristic is marked as Required field
- The item is both a sales and a production item
If none of the configuration characteristics is marked as a required field, you can carry out the configuration in the line item editor using the [Configure item] action.
Utilization in the production order
After the first validation of a production order with an item to which one or more configuration characteristics are assigned, an additional [Configure item] button becomes active in the standard toolbar. Use this button to open a dialog window to define the configuration characteristics.
Once you have defined the configuration characteristics, you can dispatch the order. By dispatching, the production structures corresponding to the configuration are generated from the bill of material and routing. Further information on the application can be found in the Production orders documentation.
Utilization in bills of material (BOM)
A maximum BOM contains all materials from which a production item can be created in all its variants. Criteria in a BOM are used to select exactly those materials that are required for the production of a configured item.
Formulas and conditions are used in the production structures so that the configuration characteristics are reflected in the production structure. Formulas and conditions are used to describe the configuration characteristic values for which the respective maximum BOM line item is accepted in the BOM to be configured. The BOM line items required for production can therefore be selected according to these values.
Further information can be found in the articles Bills of material and Conditions, formulas, substitute functions.
Utilization in routings and operations
A maximum routing contains all operations that are possible for the production of a production item in all its variants. The conditions in a routing for the respective operation are used to select exactly those operations that are required for the production of a configured item.
Formulas and conditions are used in the production structures so that the configuration characteristics are reflected in the production structure. Formulas and conditions are used to describe the configuration characteristic values for which the respective maximum routing item is accepted in the routing to be configured. The operations required for production can then be selected according to these values.
Further information can be found in the documentation Routings, Operations, and Conditions, formulas, substitute functions.
