Topic overview
All processes associated with the accrual of goods and services from external partners are mapped in the purchasing process.
A central element in the purchasing process is the purchase order. Purchase orders reflect the authorization for a supplier to deliver required material and non-material goods. Frequently, the order is preceded by a decision-making process that is based on a determination of the demand. This, in turn, often leads to supplier quotations submitted in response to purchasing RFQs. The decision-making process should thereby ensure that the optimal supplier is found. In doing so, consideration is given to delivery of the proper goods to the proper location in the proper quantity and at the proper time. Normally, the best conditions and the best price also play a decisive role in this process.
The purchase order describes the range of services of the order. The Purchase order document and Purchase order change document vouchers can be used to communicate the details of the purchase order to the supplier. Optionally, the reply from the supplier, with or without deviations, can be entered as the order confirmation.
The ordered goods become expected or undelivered goods. When goods are delivered, the user enters the quantities of the incoming items in the Receipts of goods application in the Inventory Management framework. Posting of the receipt of goods normally adds the delivered items to the inventory. Incoming invoices are checked and the values for the delivered items are entered as well as synchronized in the Supplier invoices application.
This article provides an overview of the overall purchasing process.
Definitions of terms
Consignment
In consignment, the goods of a supplier (consigner) are made available in a consignment warehouse directly on their customer’s (the consignee’s) premises. The business transaction and the transfer of ownership only take place upon the issue of the goods from the consignment warehouse, i.e. the customer’s use or resale of the goods. Such issue is referred to as consignment withdrawal. At agreed intervals, the customer informs the supplier about the consignment withdrawals in respective consignment withdrawal declarations. On the basis of these withdrawal declarations, invoices will be issued. From the purchasing perspective, this type of business is referred to as supplier consignment; from the sales perspective, it is referred to as customer consignment.
Contract release (order)
The assignment of contract line items to order line items in the sales or purchase order is also known as contract release. This contract release status of the contract line items results from this assignment, according to the contract category concerned.
Dunning letter
A dunning letter is a customer reminder to the supplier to render a service that is due.
Purchase order
A purchase order is a request to a supplier to perform services or deliver goods at a specified time. A purchase order may contain information about the item, price, quantity, delivery date, terms of payment and delivery, and the delivery address. Purchase orders can be referenced to purchasing RFQs in the system and therefore be part of a voucher references chain.
Purchase order document
A purchase order document is the voucher document for the purchase order. It is used to inform the supplier about the agreements of the purchase order made.
Purchase order confirmation
The purchase order confirmation is an external voucher document with which a partner with Supplier partner role confirms or rejects the acceptance of a purchase order document or makes a recommendation for modification. The purchase order confirmation usually contains data about the ordered items, quantities, prices, conditions and dates.
Purchasing RFQ
A purchasing RFQ is a request for a quotation addressed to one or more suppliers. A purchasing RFQ usually contains information about the item, quantity, delivery date, delivery address, and quotation deadline.
Receipt of goods
An incoming delivery is recorded in the system in a receipt of goods voucher, where item, quantity, and receipt of goods date are specified. Receipts of goods always have an order reference.
Return of goods slip
The return of goods slip contains a list of the items that have to be returned.
Supplier contracts
A supplier contract is a general contractual agreement on supplies of goods or services between a customer and a supplier. A supplier contract is always identified by a contract category, such as Fixed quantity or Fixed date. It therefore specifies when or with which event a contract is completed. A contract release can only take place by using a purchase order.
Supplier invoice
The supplier invoice contains a list of the payable amounts for delivered or yet to be delivered items. The supplier invoice is an external voucher; it may also be a credit note.
Supplier quotations
A supplier quotation is an offer made by a supplier for requested items. A supplier quotation contains information about the item, price, quantity, delivery date, terms of payment and delivery, and the delivery address. A limit can be placed on a quotation by specifying a binding period. Supplier quotations can be referenced to purchasing RFQs in the system and therefore be part of a voucher references chain.
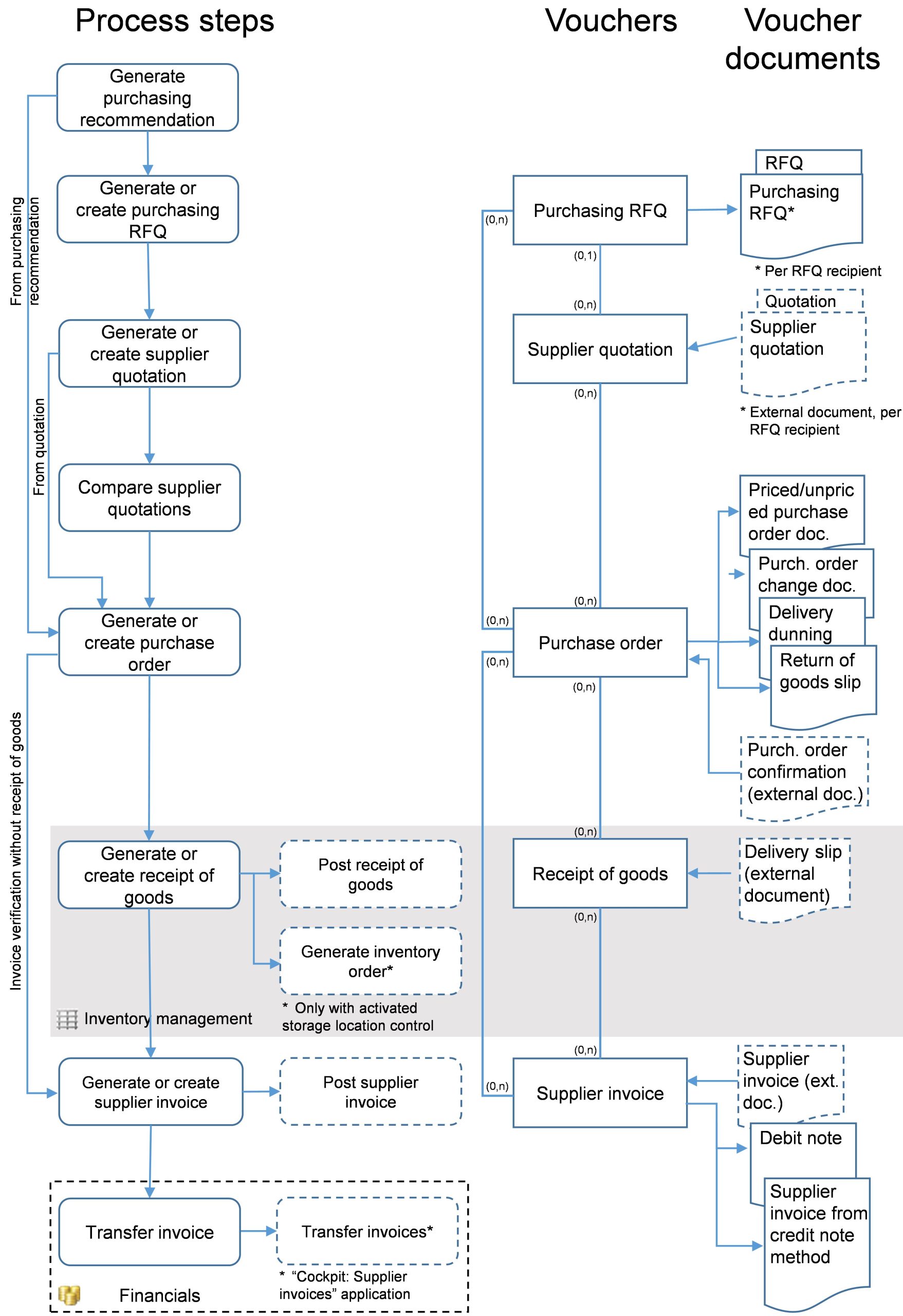
Voucher references chains
The voucher references chain displays the references of the logically connected data sets. This allows linked vouchers to be traced to a business event. The voucher references chain maps the vouchers primarily in their logical order and secondarily in their chronological order. A typical voucher references chain reflects the sequence of actions of a business process, such as sales quotation, sales order, picking, delivery, and invoicing.
Processes and voucher references chain
The ERP processes for purchasing and any resulting relationships with other applications and business entities are described below.
Process overview
The diagram below gives an overview of possible purchasing processes. The important elements of the purchasing process are explained subsequently.
Besides, various processes will be described in more detail in the following chapters:
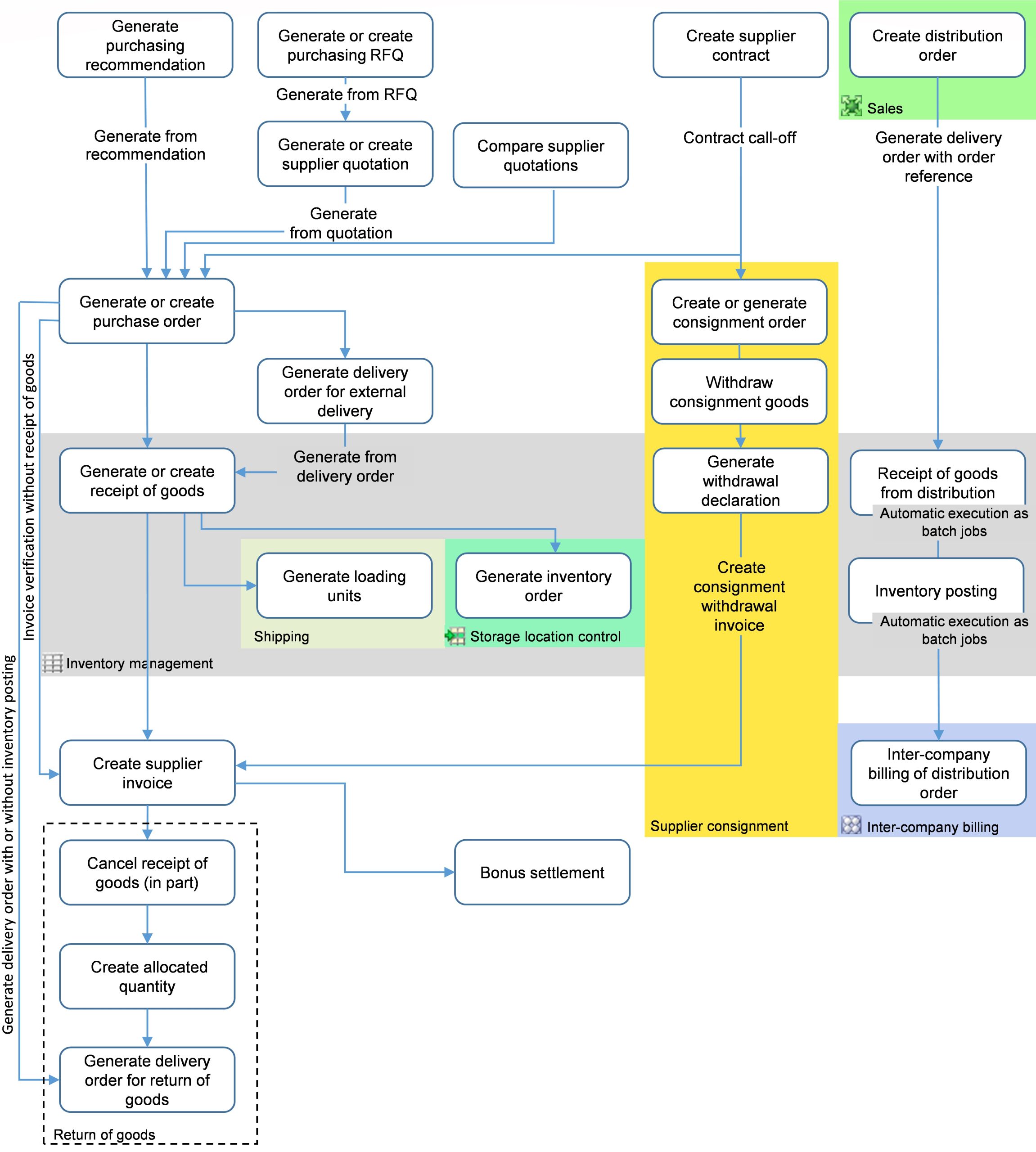
Purchase orders
Purchase orders are the central vouchers in purchasing. They can result from the following actions:
- Manual creation in the Purchase orders application
- Generation from a supplier quotation in the Purchase orders application or in the Compare supplier quotations application
- Import via the functions of the Business Integration Service
- Generation from purchasing recommendations
The sequence of possible follow-up processes can be specified in the purchase order types. Thus, you may decide, for example, whether external deliveries, such as the picking up of ordered goods, can be initiated through purchase orders.
The relationships between vouchers are shown in the voucher references chain of the applications. The voucher references chain is available for both the header and individual line items. Further information can be found in the Voucher references chain chapter.
Purchasing recommendations
Purchasing recommendations can be retrieved by the system and generated as follows:
- In the Calculate purchasing recommendations application within the Purchasing framework
- In the Generate purchasing recommendations application after completing the planning in the Material requirements planning application within the Planning framework
Based on the purchasing recommendations, purchasing RFQs can be generated for the suppliers in order to solicit supplier quotations. Another option is to generate purchase orders directly from the purchasing recommendations. In this case, it is not required to solicit supplier quotations.
Supplier contracts
Supplier contracts can be used as precursor to a purchase order. A contract is a contractual framework agreement governing deliveries of goods or services. In a contract, a customer agrees to purchase certain quantities of goods or values from a supplier over a certain time period. In return, the supplier is obliged to deliver the items in the contracted quantities or value in the agreed time period. Prices and conditions are agreed upon in the contract. A contract is beneficial not only for specifying a price for an item but also for monitoring of the conditions agreed upon in the contract.
Contracts are used by means of assignments in a purchase order. These assignments are also referred to as contract release orders. Receipts of goods cannot be entered and posted with direct reference to a contract; an order line item is always required. A supplier contract can also be generated from a supplier quotation. For more information on supplier contracts, refer to the Supplier contracts article.
Purchasing RFQs and supplier quotations
When the required goods have been manually determined, the process of manually creating a purchasing RFQ to the suppliers starts. The incoming quotations are compared using the Compare supplier quotations application in the Purchasing framework. The best quotation is determined and a purchase order is generated from it.
Purchase order documents, purchase order change documents, and purchase order confirmations
To transmit the content of a purchase order to the supplier, a purchase order document can be output and sent. After the purchase order and the purchase order document resulting from it have been changed, a purchase order document of the Purchase order change document category can be output. Changes may include the adding of new line items and the modifying or deleting of existing line items. A purchase order change document serves to notify the supplier of changed order line items. It can also be used when a purchase order has changed for which a purchase order change document has already been output and sent. In this case, the changes are determined based on the purchase order change document.
You can use a purchase order to define whether a purchase order confirmation of the supplier is required. The purchase order confirmation documents the reporting of a supplier on a generated purchase order document or purchase order change document. This reporting can be, for example, the full acceptance of the purchase order document or it can contain another delivery date. You manually create the purchase order confirmation transmitted by the supplier in the application of the same name or you generate it from the purchase order document. If a purchase order confirmation is due, you can output a confirmation reminder and send it to the supplier.
You have also the possibility to output a delivery dun in case of a delayed delivery and send it to the supplier.
Receipt of goods and supplier invoices
The receipt of ordered goods is created using the Receipt of goods application in the Inventory management framework. The supplier invoice is created as well. In this process, the receipt of goods and the supplier invoice are assigned to the purchase order. If the invoice or a partial invoice is issued and settled before the delivery, the sequence may also differ. By posting the receipt of goods and the supplier invoice as well as an inventory order, if any, the purchasing process is closed.
If the values in a supplier invoice and those saved in the purchase order are not the same, you can also generate a credit note for the difference (correction supplier invoice). This credit note can be sent as debit note to the supplier.
General purchasing process
The standard order is a purchase order of the Order category, based on which items are purchased from a supplier and delivered to a warehouse. The order contains all details on the supplier, delivery partner, invoicing party as well as all commercial agreements, such as delivery terms, shipping terms, payment terms, prices and discounts, items, and quantities. Determining data on the various actions is to be specified in the order type. For more information on the determining elements, refer to the Sales orders and Sales order types articles.
Supplier consignment and consignment orders
The term Supplier consignment refers to a logistic process with a supplier storing items in the warehouse of the customer so that the customer can take items directly from it. Only after the customer has taken items from the consignment warehouse, this results in the transfer of ownership and the issuance of respective invoices.
For carrying out a consignment business, the customer and the supplier enter into a consignment agreement on specific items, sites, and periods. The agreement is created based on a supplier contract of the Consignment category. To call off the consignment goods at the supplier, the purchase order of the Consignment order category is available. Within the scope of this consignment business, the customer informs the supplier at agreed-upon intervals about quantities taken, e.g., with each withdrawal or in total per day or period. To do so, the customer uses consignment withdrawal declarations. For more information, see the Introduction: Supplier consignment article.
Distribution
If internal suppliers are responsible for purchasing, you have two possibilities:
- An internal supplier is used in the purchase order; the process is the same as when using external suppliers for purchasing.
- The distribution of goods is simplified by means of a distribution recommendation and a distribution order generated from it. For more information, see the Distribution recommendations, Introduction: Distribution orders, and Receipts of goods from distribution articles
If the internal supplier belongs to another firm of the own company, inter-company billing will be required. For more information, refer to the Introduction: Inter-company billing article.
Returns
Returning delivered items to the supplier may include the following processes:
- Returning of goods already paid and put away, including subsequent credit note (return with inventory posting)
- Returning of goods not yet paid nor put away (return without inventory posting)
- Credit notes without return of goods (return without inventory posting)
The ERP system differentiates between returns with inventory posting and returns without inventory posting. The return with inventory posting causes the issued quantities to be posted, and is the opposite of posting the receipt of goods. Whereas the return without inventory posting only results in the outputting of a voucher document – the return of goods slip. If goods need to be deducted in such a case, this is done via a manual inventory posting (manual correction posting), a receipt of goods cancelation, or a partial receipt of goods cancelation.
The Purchase orders and Receipts of goods applications provide various actions for returns, which are mainly used depending on the constellation of the receipt of goods, i.e. whether items managed by identifiers are involved and whether the goods have been received at a subdivided warehouse.
For further information on the various return processes in purchasing and the options for processing returns, see the Return of goods and credit notes article.
Voucher references chain
In the voucher references chain of the purchase order, the below upstream and downstream vouchers will be visible if they are connected through a voucher reference. In most cases, the line items of the vouchers are connected as well. For each voucher, all connected vouchers are displayed. So for instance, a referenced supplier contract is listed in the voucher references chain for a purchase order and this purchase order, in turn, is shown in the voucher references chain of the supplier contract.
The progress of the purchasing process is visible in the voucher status. The purchase order is the central voucher here that shows the status for all subsequent processes at the line item level and in the header.
| Voucher | Conditions for display |
|---|---|
| Supplier contract | The supplier contract is shown in the voucher references chain of the purchase order if a purchase order line item was assigned to a supplier contract line item. |
| Supplier quotation | If a purchase order was generated from a supplier quotation, this quotation is displayed in the voucher references chain. |
| Purchase order document Purchase order change document | If an unpriced or priced purchase order document or a subsequent purchase order change document was generated for the purchase order, such voucher documents are shown in the voucher references chain. |
| Purchase order confirmation | If a purchase order confirmation was generated for a purchase order document or a purchase order change document, it is shown in the voucher references chain. |
| Receipt of goods | If a receipt of goods line item was assigned a purchase order line item and the receipt of goods was saved, this reference is shown in the voucher references chain. |
| Delivery order | If a delivery order was generated from a purchase order for an external delivery, e.g., for picking up goods, the delivery order is shown in the voucher references chain. |
| Supplier invoice | If a supplier invoice line item was assigned a purchase order line item, this reference is shown in the voucher references chain. |
| Customer invoice | If the purchase order was cleared internally, the customer invoice of the internal supplier is shown in the voucher references chain of the purchase order. |
Bonus settlement
Bonuses in purchasing are subsequent payments for a part of a supplier’s turnover over a specific time period. The payment can be made actively by debiting the supplier’s account or through a credit note. Bonus-relevant turnovers are based on supplier invoices or credit notes. Purchasing bonus agreements can be made to specify the invoice line items that are subject to bonuses and the suppliers with whom agreements have been entered into. For more information, refer to the Introduction: Purchasing bonus article.
