Overview
The COMARCH ERP Enterprise system’s Quality Management framework enables the quality management process for goods receipt. This process can be carried out before or after the goods are received and entered into the company’s warehouse. This article describes basic applications for designing and managing goods inspection processes.
The quality management framework works with other frameworks of the system, such as:
- Planning
- Production
- Inventory management
Definitions of terms
Organization – the organization within which processes are carried out in the system. This is typically the organization to which the user is currently logged in.
Parameter – a characteristic of goods or a process that is checked as part of quality management. Characteristics can be measurable (quantifiable, e.g., length, density, and gel time) or non-measurable (e.g., compliant/noncompliant or white mat).
Parameter type – specifies whether the parameter is measurable (definable with a number and unit, e.g. 30 mm, 120 s) or non-measurable (definable only by providing a description/characteristic, e.g. black mat, transparent, no discoloration).
Method – describes how to carry out inspection activities.
Control plan type – control plan type created in the Control plan types application. Any types of control plan can be created for categorizing control plans.
Control plan – a document created based on the control plan type. It provides information on the product’s controlled characteristics and contains a list of parameters to be checked using the selected methods as part of quality management. Each parameter has a specific type and expected value (scope or characteristic). The document also contains information about how important the parameter is and how many times it should be measured during the inspection.
Control plan version – if the versioning option is activated, successive versions of a control plan can be created. Each version must undergo the approval process before it can be used in the inspection process. A given control plan can only have one version with a Released status at any given time. It is possible to specify the date on which a version becomes effective. The version becomes ineffective when the next version is released. Versioning is used for minor changes to the control plan. The system maintains a record of these changes.
Inspection order type – a user-defined type of inspection order that includes a template of default data. Examples of inspection order types include re-inspection, claim inspection, and first-piece inspection.
Inspection order – a document created based on the type of inspection order. It is used to check the quality of goods in or entering the warehouse.
Number range – the number range defined in the Number ranges application. It is used to uniquely identify objects in the system. Number ranges automatically generate numbers based on a defined formula.
Critical parameter – this parameter must not be overlooked in the quality management process. It has a significant impact on the quality of the product or its production process. The field is informative and does not affect the production process.
Quality certificate – a document confirming that the finished product complies with the technical documentation requirements.
Approver – a person (or group of people) authorized to approve control plans.
Lower limit – the minimum possible value for the actual dimension within the specified range.
Upper limit – the maximum possible value for the actual dimension within the specified range.
Mandatory inspection – determines the need for quality control.
Cost unit – cost objects distinguished within an organization based on certain criteria, such as a group of products.
Cost center – the place where costs are generated. The cost center system is integrated into the company’s structure and is responsible for classifying and identifying individual expenses.
Quality Management framework-related applications
The Quality Management framework includes the following applications:
- Methods
- Parameters
- Control plan types
- Control plans
- Control plan assignments
- Inspection order types
- Inspection orders
- Inspection order postings
The Quality Management framework also offers cockpit applications that allow users to easily view and export objects added to the system (e.g. to an Excel file):
- Cockpit: Control plans
- Cockpit: Inspection orders
The Quality Management framework has two batch applications:
- Reorganization of quality management master data
- Reorganization of inspection orders
Processes/Functions
In manufacturing, quality management involves monitoring and evaluating materials and products to ensure they meet specific standards. Minimizing defects, ensuring customer satisfaction, and reducing production costs are integral parts of the production process.
The quality management framework is designed to enable the system to control specific parameters of a material or product.
The following diagram illustrates the quality control preparation process.
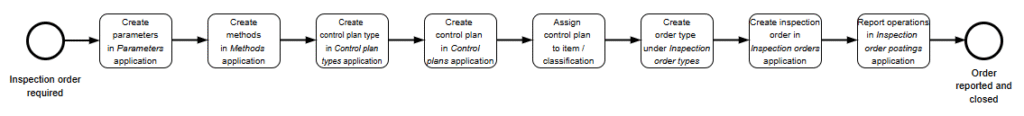
View the articles below for description of individual applications:
- Methods
- Parameters
- Control plan types
- Control plans
- Control plan assignments
- Inspection order types
- Inspection orders
- Inspection order postings
- Cockpit: Control plans
- Cockpit: Inspection orders
- Batch application: Reorganization of quality management master data
- Batch application: Reorganization of inspection orders
